출처: https://rfriend.tistory.com/289
지난번 포스팅에서는 다차원 행렬 ndarray에 축을 추가하는 방법으로 arr(:, np.newaxis, :), np.tile() 을 소개했었습니다.
이번 포스팅에서는 행렬의 행과 열을 바꾸기, 행렬의 축을 바꾸는 방법을 알아보겠습니다. 선형대수에서 보면 '전치행렬(transpose matrix)'이라는 특수한 형태의 행렬이 있는데요, 이번 포스팅이 바로 그겁니다. 행렬의 내적(inner product) 구할 때 aT*a 처럼 전치행렬과 원래 행렬을 곱할 때 전치행렬(aT)를 씁니다.
Python의 NumPy 로 부터 행렬 전치를 위해
- a.T attribute
- np.transpose(a) method
- np.swapaxes(a, 0, 1) method
의 3가지 방법을 사용할 수 있습니다.
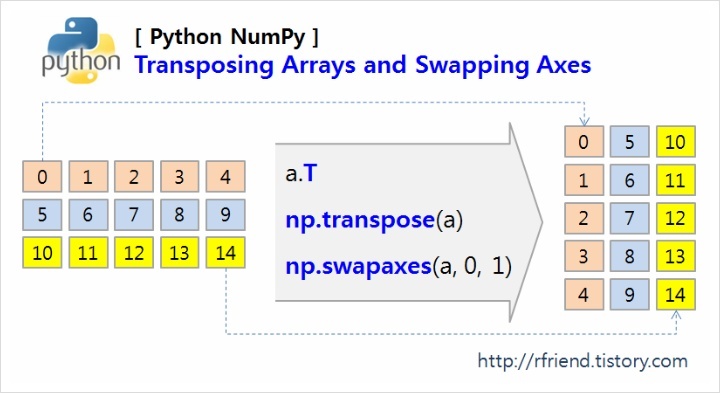
a.T attrbute, np.transpose() method, np.swapaxes() method 각각에 대해 2차원 행렬을 전치하는 간단한 예를 들어보겠습니다.
| (1-1) Transposing 2 D array : a.T attribute |
In [1]: import numpy as np In [2]: a = np.arange(15).reshape(3, 5) In [3]: a Out[3]: array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12, 13, 14]]) # (1-1) transposing 2D array : T attribute In [4]: a.T Out[4]: array([[ 0, 5, 10], [ 1, 6, 11], [ 2, 7, 12], [ 3, 8, 13], [ 4, 9, 14]]) |
| (1-2) Transposing 2D array : np.transpose() method |
In [5]: a Out[5]: array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12, 13, 14]]) # (1-2) transpose method : numpy.transpose(a, axes=None) In [6]: np.transpose(a) Out[6]: array([[ 0, 5, 10], [ 1, 6, 11], [ 2, 7, 12], [ 3, 8, 13], [ 4, 9, 14]]) |
| (1-3) Transposing 2D array : np.swapaxes() method |
In [7]: a Out[7]: array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12, 13, 14]]) # (1-3) swapaxes method : numpy.swapaxes(a, axis1, axis2) In [8]: np.swapaxes(a, 0, 1) Out[8]: array([[ 0, 5, 10], [ 1, 6, 11], [ 2, 7, 12], [ 3, 8, 13], [ 4, 9, 14]]) |
이쯤에서 NumPy의 np.dot() 으로 행렬 내적 (inner product, aT*a) 계산해볼까요?
In [9]: np.dot(a.T, a) Out[9]: array([[125, 140, 155, 170, 185], [140, 158, 176, 194, 212], [155, 176, 197, 218, 239], [170, 194, 218, 242, 266], [185, 212, 239, 266, 293]]) In [10]: np.dot(np.transpose(a), a) Out[10]: array([[125, 140, 155, 170, 185], [140, 158, 176, 194, 212], [155, 176, 197, 218, 239], [170, 194, 218, 242, 266], [185, 212, 239, 266, 293]]) In [11]: np.dot(np.swapaxes(a, 0, 1), a) Out[11]: array([[125, 140, 155, 170, 185], [140, 158, 176, 194, 212], [155, 176, 197, 218, 239], [170, 194, 218, 242, 266], [185, 212, 239, 266, 293]]) |
2차원 행렬로 전치에 대한 맛을 봤으니, 이제 3차원 행렬의 축을 바꿔보는 것으로 난이도를 높여보겠습니다. np.transpose() 와 np.swapaxes() method는 전치시키려고 하는 축을 입력해줘야 하는데요, 조금 조심해서 사용해야 합니다.
| (2-1) Transposing 3D array : a.T attribute |
In [12]: b = np.arange(24).reshape(2, 3, 4) In [13]: b Out[13]: array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]], [[12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) In [14]: b.T Out[14]: array([[[ 0, 12], [ 4, 16], [ 8, 20]], [[ 1, 13], [ 5, 17], [ 9, 21]], [[ 2, 14], [ 6, 18], [10, 22]], [[ 3, 15], [ 7, 19], [11, 23]]]) In [15]: b.T.shape Out[15]: (4, 3, 2) |
| (2-2) Transposing 3D array : np.transpose() method |
np.transpose() method는 축을 바꾸고 싶은 위치, 순서를 분석가가 마음대로 지정할 수 있다는 측면에서 T attribute 보다 자유도가 높습니다. (처음엔 좀 헷갈리고 이해가 잘 안가는 면도 있지만요)
# shape (2, 3, 4) In [16]: b Out[16]: array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]], [[12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) # shape(2, 3, 4) => shape (4, 3, 2) In [17]: np.transpose(b) Out[17]: array([[[ 0, 12], [ 4, 16], [ 8, 20]], [[ 1, 13], [ 5, 17], [ 9, 21]], [[ 2, 14], [ 6, 18], [10, 22]], [[ 3, 15], [ 7, 19], [11, 23]]]) # shape(2, 3, 4) => shape (4, 3, 2) In [18]: np.transpose(b, (2, 1, 0)) Out[18]: array([[[ 0, 12], [ 4, 16], [ 8, 20]], [[ 1, 13], [ 5, 17], [ 9, 21]], [[ 2, 14], [ 6, 18], [10, 22]], [[ 3, 15], [ 7, 19], [11, 23]]]) In [19]: b.shape Out[19]: (2, 3, 4) In [20]: np.transpose(b).shape Out[20]: (4, 3, 2) |
| (2-3) Transposing 3D array : np.swapaxes() method |
In [21]: b Out[21]: array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]], [[12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) In [22]: b.shape Out[22]: (2, 3, 4) # shape(2, 3, 4) => shape(4, 3, 2) In [23]: np.swapaxes(b, 0, 2) Out[23]: array([[[ 0, 12], [ 4, 16], [ 8, 20]], [[ 1, 13], [ 5, 17], [ 9, 21]], [[ 2, 14], [ 6, 18], [10, 22]], [[ 3, 15], [ 7, 19], [11, 23]]]) In [24]: np.swapaxes(b, 0, 2).shape Out[24]: (4, 3, 2) |
np.transpose() 와 np.swapaxes() method를 사용해서 전치시키려는 축의 순서를 위의 예시와는 조금 다르게 바꿔서 해보겠습니다. 축(axes)의 순서를 바꿔서 입력해주면 됩니다. (말로 설명하기 좀 어려운데요, 아래 예와 위의 예를 유심히 살펴보시기 바랍니다)
In [25]: b Out[25]: array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]], [[12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) In [26]: b.shape Out[26]: (2, 3, 4) # shape(2, 3, 4) => shape(3, 2, 4) In [27]: np.transpose(b, (1, 0, 2)).shape Out[27]: (3, 2, 4) In [28]: np.transpose(b, (1, 0, 2)) Out[28]: ararray([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [12, 13, 14, 15]], [[ 4, 5, 6, 7], [16, 17, 18, 19]], [[ 8, 9, 10, 11], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) |
위의 [28]번 np.transpose(b, (1, 0, 2)) 와 똑같은 결과를 얻을 수 있는 방법으로 np.swapaxes(b, 1, 0)을 사용하면 됩니다.
In [29]: b Out[29]: array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]], [[12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) In [30]: b.shape Out[30]: (2, 3, 4) In [31]: np.swapaxes(b, 1, 0).shape Out[31]: (3, 2, 4) In [32]: np.swapaxes(b, 1, 0) Out[32]: ararray([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [12, 13, 14, 15]], [[ 4, 5, 6, 7], [16, 17, 18, 19]], [[ 8, 9, 10, 11], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) |
많은 도움 되었기를 바랍니다.
출처: https://rfriend.tistory.com/289 [R, Python 분석과 프로그래밍의 친구 (by R Friend)]
'IT기술 관련 > A.I 인공지능' 카테고리의 다른 글
| AI 이미지 생성 사이트 정리 (0) | 2023.03.20 |
|---|---|
| Best 10 AI 이미지 제작 사이트 (0) | 2023.03.20 |
| Training and Testing data sets (0) | 2021.02.15 |
| Sigmoid 대신 ReLU? 상황에 맞는 활성화 함수 사용하기 (0) | 2021.02.15 |
| 머신 러닝 - batch size 적절하게 조절하기 (0) | 2021.02.09 |